1.3 Why is data archiving important?
Archiving data is beneficial both for producers of data and the research community.
Access to data
Data archives make research data available for reuse as much as possible under the FAIR principles (CESSDA Training Team 2017-2022; Deutz, Daniella Bayle et al. 2020; Wilkinson et al. 2016). You can learn more about fairness of data in Chapter 5 of this guide. Some data can be accessed only under strict conditions, for example when the data contains personal information (see the section What is archived?). Archives have various data access categories that data producers can choose, when they deposit their data (see the section How does an archive make data available?)”.
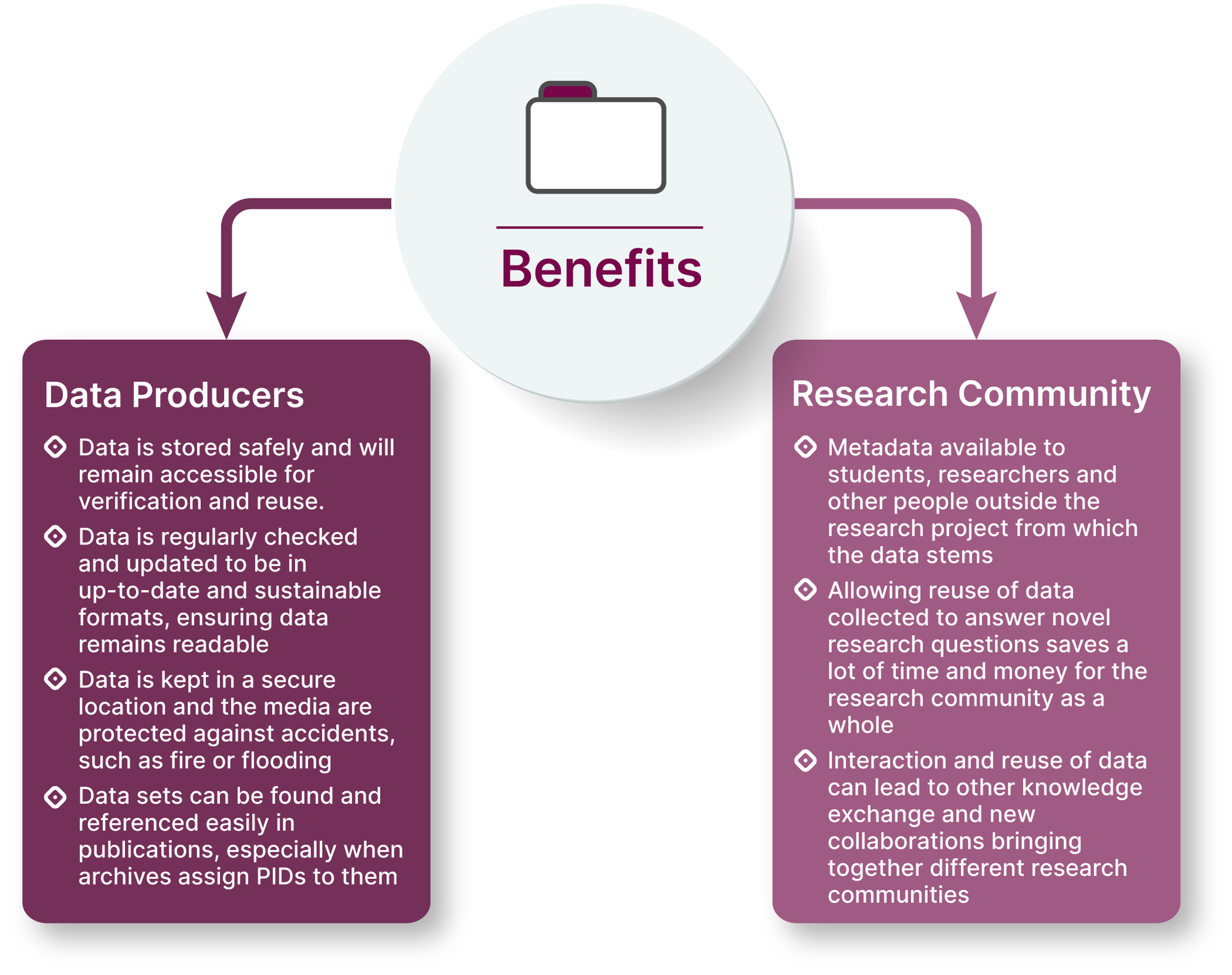
The benefits of data archiving for data producers are:
- Trustworthy data archives store data on reliable media and ensure that it is not lost, will remain accessible for verification and reuse, and is preserved. (No risk for the data producer of losing valuable data by losing flash drives, accidentally deleting files, or not remembering a password to an old laptop.)
- Data formats used during data production often quickly become outdated, which renders the data unreadable after some time. In data archives, data is regularly checked and updated to be in up-to-date and sustainable formats, ensuring data remains readable (see section 1.7 What is archived?).
- Archives keep data in a secure location and protect the media against accidents, such as fire or flooding. Data archives ensure that the data will not be damaged.
- Datasets can be found and referenced easily in publications, especially when archives assign PIDs to them.
The benefits of data archiving for the research community are:
- Data archives make data and related metadata available to students, researchers, and other people outside the research project from which the data stems. These users can thus benefit from datasets collected by other researchers and reuse them for their research or teaching purposes.
- Allowing researchers to reuse data collected by other researchers to answer novel research questions saves a lot of time and money for the research community as a whole.
- Interaction and reuse of data can lead to other knowledge exchange and possible new collaborations in the future, bringing together different communities.
You can read more about the benefits of managing and archiving data in 'DMEG - Chapter 1 Plan' and 'DMEG - Chapter 6 Archive and Publish' (CESSDA Training Team 2017-2022).
Quality of data in data archives
Although archives do not guarantee the scientific quality of the data itself, they provide essential information about the data so that users can judge it for themselves. You can find the necessary information for reuse in the metadata that contains a description of the methodology used for data collection as well as other information about the dataset.
Find out more about your archive
Here are some questions that you can ask yourself to learn more about your archive:
- Can you think of other benefits that your archive provides for its users by archiving data?
- How does your archive ensure quality and access to data?
- What kind of support does your archive offer to data producers and users about data archiving and its benefits?